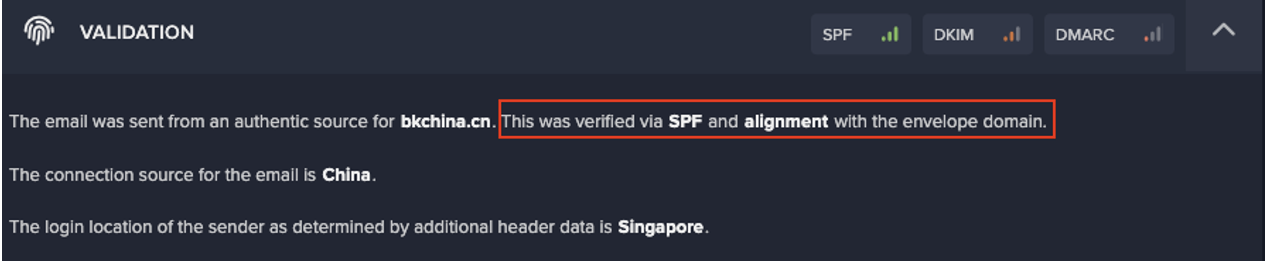
About the AI Cybersecurity Report
Darktrace surveyed 1,800 CISOs, security leaders, administrators, and practitioners from industries around the globe. Our research was conducted to understand how the adoption of new AI-powered offensive and defensive cybersecurity technologies are being managed by organizations.
This blog continues the conversation from “The State of AI in Cybersecurity: Unveiling Global Insights from 1,800 Security Practitioners” which was an overview of the entire report. This blog will focus on one aspect of the overarching report, the impact of AI on cybersecurity solutions.
To access the full report, click here.
The effects of AI on cybersecurity solutions
Overwhelming alert volumes, high false positive rates, and endlessly innovative threat actors keep security teams scrambling. Defenders have been forced to take a reactive approach, struggling to keep pace with an ever-evolving threat landscape. It is hard to find time to address long-term objectives or revamp operational processes when you are always engaged in hand-to-hand combat.
The impact of AI on the threat landscape will soon make yesterday’s approaches untenable. Cybersecurity vendors are racing to capitalize on buyer interest in AI by supplying solutions that promise to meet the need. But not all AI is created equal, and not all these solutions live up to the widespread hype.
Do security professionals believe AI will impact their security operations?
Yes! 95% of cybersecurity professionals agree that AI-powered solutions will level up their organization’s defenses.
Not only is there strong agreement about the ability of AI-powered cybersecurity solutions to improve the speed and efficiency of prevention, detection, response, and recovery, but that agreement is nearly universal, with more than 95% alignment.
This AI-powered future is about much more than generative AI. While generative AI can help accelerate the data retrieval process within threat detection, create quick incident summaries, automate low-level tasks in security operations, and simulate phishing emails and other attack tactics, most of these use cases were ranked lower in their impact to security operations by survey participants.
There are many other types of AI, which can be applied to many other use cases:
Supervised machine learning: Applied more often than any other type of AI in cybersecurity. Trained on attack patterns and historical threat intelligence to recognize known attacks.
Natural language processing (NLP): Applies computational techniques to process and understand human language. It can be used in threat intelligence, incident investigation, and summarization.
Large language models (LLMs): Used in generative AI tools, this type of AI applies deep learning models trained on massively large data sets to understand, summarize, and generate new content. The integrity of the output depends upon the quality of the data on which the AI was trained.
Unsupervised machine learning: Continuously learns from raw, unstructured data to identify deviations that represent true anomalies. With the correct models, this AI can use anomaly-based detections to identify all kinds of cyber-attacks, including entirely unknown and novel ones.
What are the areas of cybersecurity AI will impact the most?
Improving threat detection is the #1 area within cybersecurity where AI is expected to have an impact.
The most frequent response to this question, improving threat detection capabilities in general, was top ranked by slightly more than half (57%) of respondents. This suggests security professionals hope that AI will rapidly analyze enormous numbers of validated threats within huge volumes of fast-flowing events and signals. And that it will ultimately prove a boon to front-line security analysts. They are not wrong.
Identifying exploitable vulnerabilities (mentioned by 50% of respondents) is also important. Strengthening vulnerability management by applying AI to continuously monitor the exposed attack surface for risks and high-impact vulnerabilities can give defenders an edge. If it prevents threats from ever reaching the network, AI will have a major downstream impact on incident prevalence and breach risk.
Where will defensive AI have the greatest impact on cybersecurity?
Cloud security (61%), data security (50%), and network security (46%) are the domains where defensive AI is expected to have the greatest impact.
Respondents selected broader domains over specific technologies. In particular, they chose the areas experiencing a renaissance. Cloud is the future for most organizations,
and the effects of cloud adoption on data and networks are intertwined. All three domains are increasingly central to business operations, impacting everything everywhere.
Responses were remarkably consistent across demographics, geographies, and organization sizes, suggesting that nearly all survey participants are thinking about this similarly—that AI will likely have far-reaching applications across the broadest fields, as well as fewer, more specific applications within narrower categories.
Going forward, it will be paramount for organizations to augment their cloud and SaaS security with AI-powered anomaly detection, as threat actors sharpen their focus on these targets.
How will security teams stop AI-powered threats?
Most security stakeholders (71%) are confident that AI-powered security solutions are better able to block AI-powered threats than traditional tools.
There is strong agreement that AI-powered solutions will be better at stopping AI-powered threats (71% of respondents are confident in this), and there’s also agreement (66%) that AI-powered solutions will be able to do so automatically. This implies significant faith in the ability of AI to detect threats both precisely and accurately, and also orchestrate the correct response actions.
There is also a high degree of confidence in the ability of security teams to implement and operate AI-powered solutions, with only 30% of respondents expressing doubt. This bodes well for the acceptance of AI-powered solutions, with stakeholders saying they’re prepared for the shift.
On the one hand, it is positive that cybersecurity stakeholders are beginning to understand the terms of this contest—that is, that only AI can be used to fight AI. On the other hand, there are persistent misunderstandings about what AI is, what it can do, and why choosing the right type of AI is so important. Only when those popular misconceptions have become far less widespread can our industry advance its effectiveness.
To access the full report, click here.
.png)