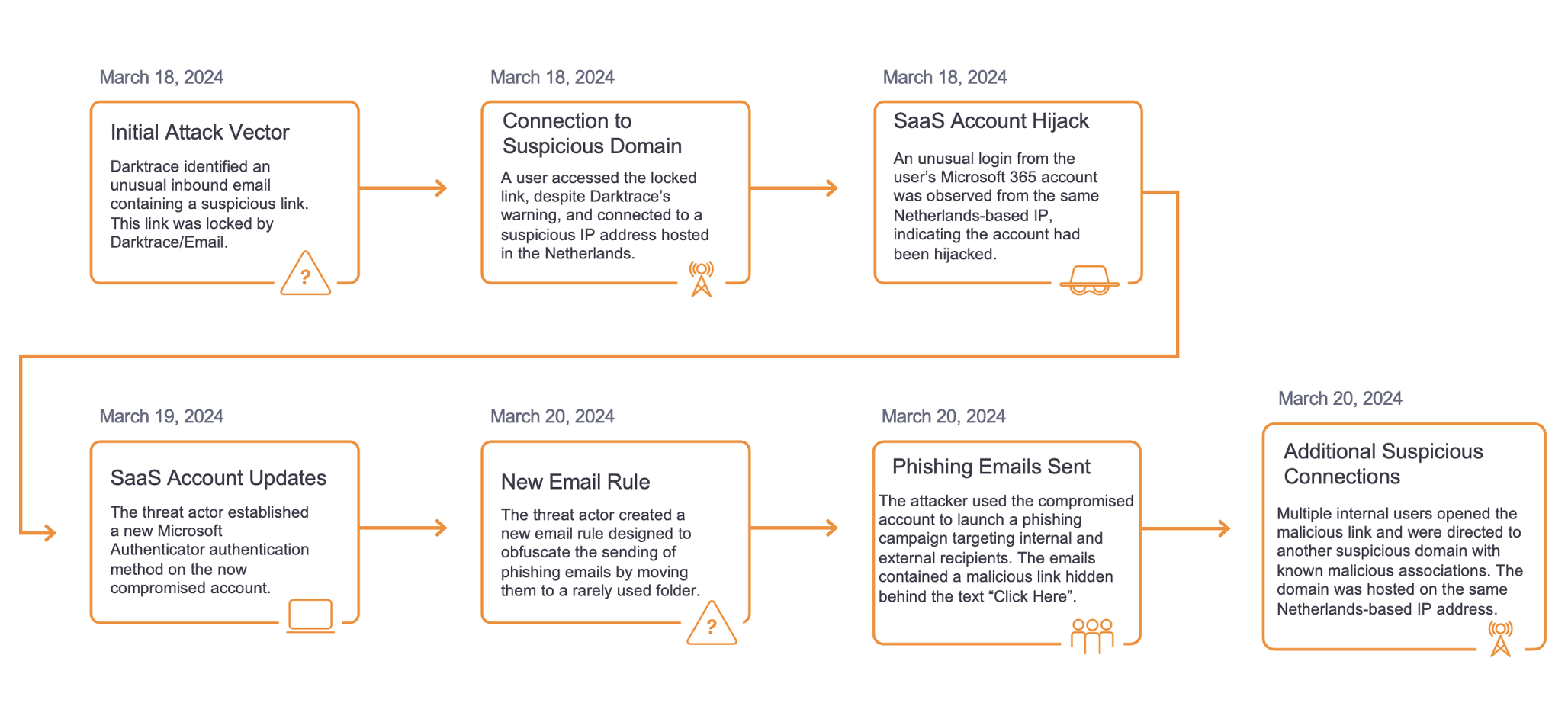
はじめに
昨年は、サイバー脅威の状況が依然として複雑で予測困難であることを示す、さらなる証拠となりました。不確実なアトリビューション、新しいエクスプロイト、急速なマルウェア開発の狭間で、セキュリティの取り組みをどこに集中させるべきかを知ることが難しくなってきています。2021年の最大のサプライズの1つは、悪名高いEmotetボットネットの再来でした。これは、業界の特性や地域を無視し、一見すると無差別に企業をターゲットにしたキャンペーンの例です。1月に法執行機関がEmotetをテイクダウンしてからわずか10か月後、11月に新たなEmotetの活動がセキュリティ研究者によって発見されました。この活動は2022年の第1四半期まで続きましたが、このブログでは、Darktraceの脅威インテリジェンスユニットによる調査結果を通じて、この時期を探っていきます。
2019年にさかのぼると、EmotetはTrickbotペイロードを配信し、最終的に感染したデバイスにRyukランサムウェア株を展開することが知られています。この相互接続性は、脅威グループのヒドラのような性質を浮き彫りにし、1つを排除しても(たとえ本格的な法執行機関の介入があっても)脅威として排除されることはなく、脅威の状況がより安全になることを示すものでもないことを示しました。
Emotet が復活したとき、予想通り、最初の感染経路の1つは、既存の Trickbot のインフラを活用することでした。しかし、元の攻撃とは異なり、全く新しいフィッシングキャンペーンが採用されました。

当初のEmotet感染と似ていますが、新しい感染の波は2つのカテゴリーに分類されています。エポック4とエポック5です。Darktraceが展開するグローバルな顧客環境では、エポック4 に関連する Emotet 感染が最も多く発生しているようです。影響を受けた顧客環境は、製造業やサプライチェーン、接客業や旅行業、行政、技術や通信、医療など、幅広い国や業種で見られました(図 1)。また、従業員数も250人以下から5,000人以上の企業までさまざまで、企業の属性や規模はターゲティングの要因にはなっていないようです。
エポック1-3とエポック4-5の主な違い
Emotetエクスプロイトの内部構造に関する幅広いセキュリティ調査に基づき、エポック4/5とその前の世代の間にいくつかの重要な違いがあることが確認されました。新しいエポックでは、以下のものが使用されていました:
- Microsoft の文書形式が異なる(OLEとXMLベース)。
- 通信のための異なる暗号化アルゴリズム。新しいエポックでは、C2設定ファイル [2] に含まれる公開暗号鍵で楕円曲線暗号(ECC)[1] を使用しました。これは、これまでのRSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)鍵の暗号化方式とは異なるものでした。
- Control Flow Flatteningは、検知やリバースエンジニアリングを困難にする難読化技術として利用されていました。これは、プログラムの制御フローを隠蔽することによって行われます [3]。
- C2通信は230以上のユニークなIPに向けられており、すべて新しいエポック4と5に関連していることから、新しいC2インフラが観察されました。
エポック4-5の新機能に加え、Darktrace は新たなキャンペーンの影響を受けたそれらの展開に意外な共通点があることを検知しました。これには、Emotetの新しいインフラストラクチャへの自己署名付きSSL接続と、複数の稀な外部エンドポイントへのマルウェアスパム活動が含まれていました。これらのアウトバウンドコミュニケーションに先立ち、複数の展開におけるデバイスが、Emotet に関連するペイロード (アルゴリズムで生成された DLL ファイル) をダウンロードしたことが検知されました。
Emotet 復活キャンペーン

1. 最初の侵害
復活活動における最初の侵入経路は、ほぼ間違いなく、Trickbotインフラストラクチャまたは成功したフィッシング攻撃です(図2)。最初の侵入後、このマルウェア株は、マクロ化されたファイルを介してペイロードのダウンロードを開始し、その後のマルウェアのダウンロードのためにPowerShellを起動するために使用されます。
ダウンロードの後、Emotet の C2 インフラとの悪意のある通信が、スパムモジュールの活動とともに観測されました。Darktrace 内で、主要なテクニックが観察され、以下に文書化されています。
2. 足場を固めるバイナリ ダイナミック リンク ライブラリ(.dll)とアルゴリズムによるファイル名の生成
Emotet のペイロードはポリモーフィック型であり、アルゴリズムで生成されたファイル名を含んでいます。また、導入した環境では、www[.]arkpp[.]com という疑わしいホスト名を含む HTTP GET リクエストや、以下のような Emotet 関連のサンプルが確認されています。
- hpixQfCoJb0fS1.dll (SHA256ハッシュ:859a41b911688b00e104e9c474fc7aaf7b1f2d6e885e8d7fbf11347bc2e21eaa)
- M0uZ6kd8hnzVUt2BNbRzRFjRoz08WFYfPj2.dll (SHA256 ハッシュ:9fbd590cf65cbfb2b842d46d82e886e3acb5bfecfdb82afc22a5f95bda7dd804)
- TpipJHHy7P.dll (SHA256 ハッシュ:40060259d583b8cf83336bc50cc7a7d9e0a4de22b9a04e62ddc6ca5dedd6754b)
これらのDLLファイルは、rundll32[.]exeやregsvr32[.]exe などのWindowsプロセスに依存して実行されるEmotetローダーの配布を表している可能性が高いです。
3. 足場を確立するEmotet C2 サーバーへのアウトバウンド SSL 接続
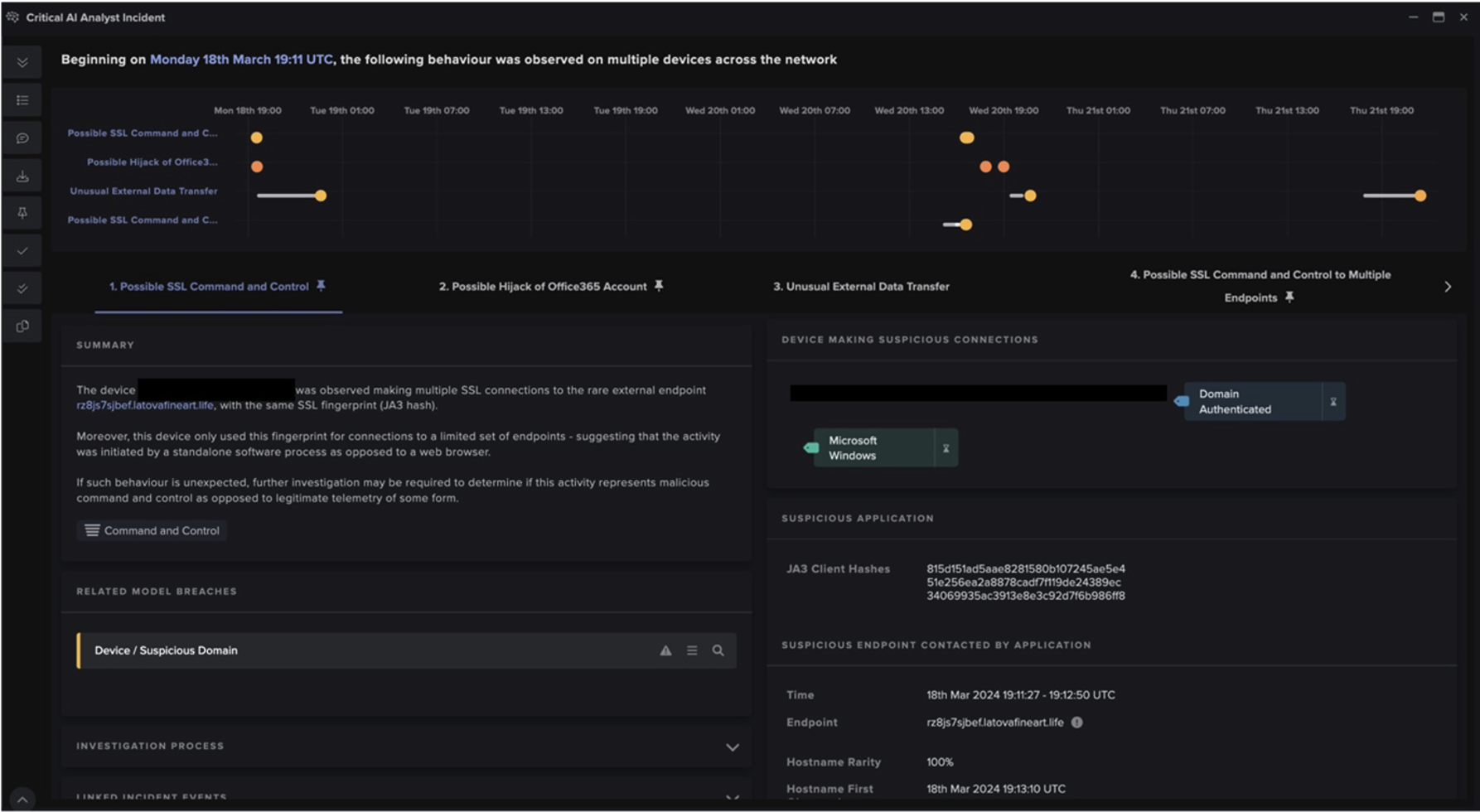
EmotetのC2通信のための明確なネットワークIoCは、CN=example[.]com,OU=IT Department,O=Global Security,L=London,ST=London,C=GB と一致する証明書発行者と件名を使用し、共通のJA3クライアントフィンガープリント(72a589da586844d7f0818cce684948ea)を使用して自己署名SSLを含みました。主なC2通信は、エポック5ではなくエポック4に分類されるインフラに関与していることが確認されました。通信内容は暗号化されていましたが、ネットワーク接続の詳細はC2活動の検知に十分なものでした(図3)。

TCPポート25、465、587でのアウトバウンドSSLおよびSMTP接続
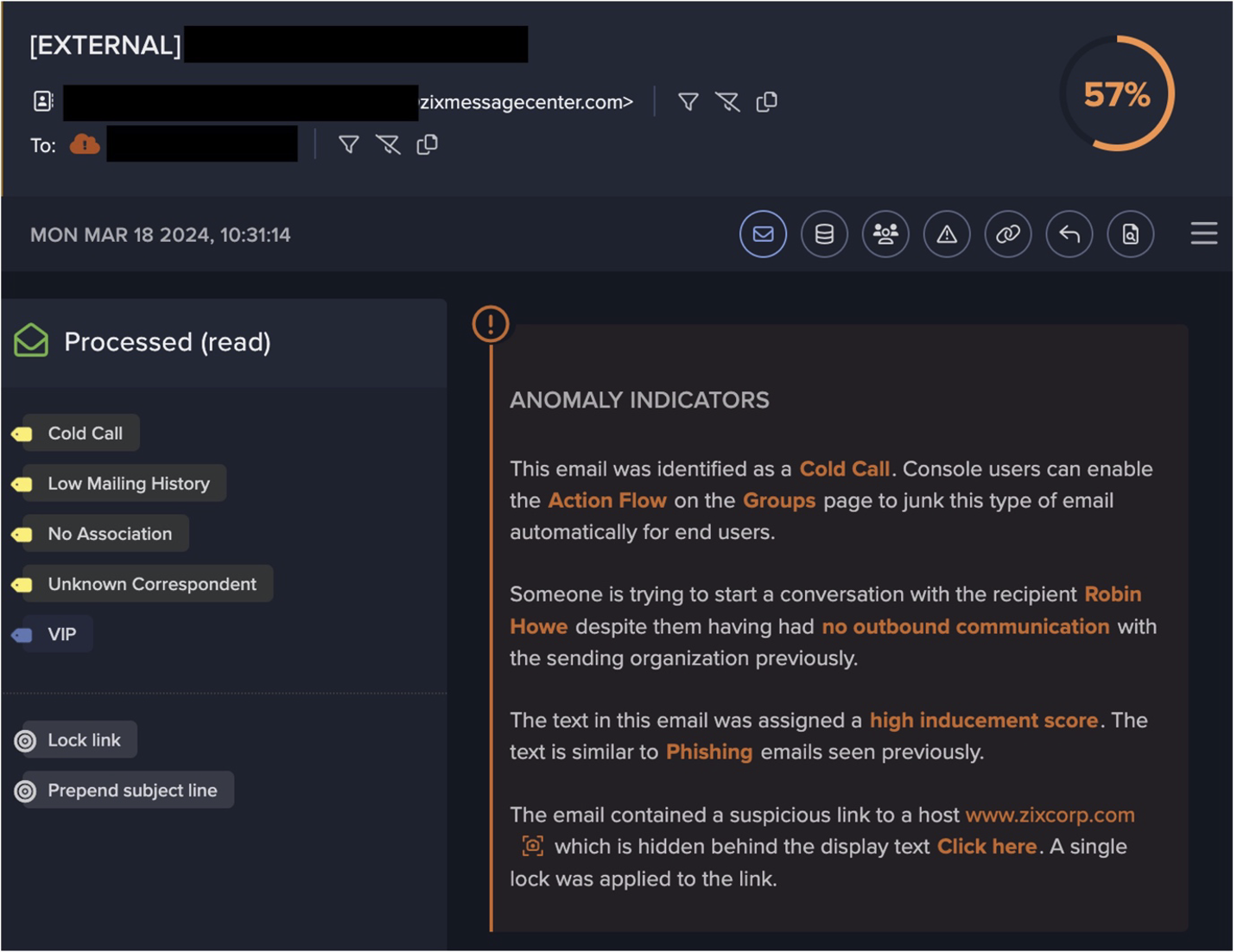
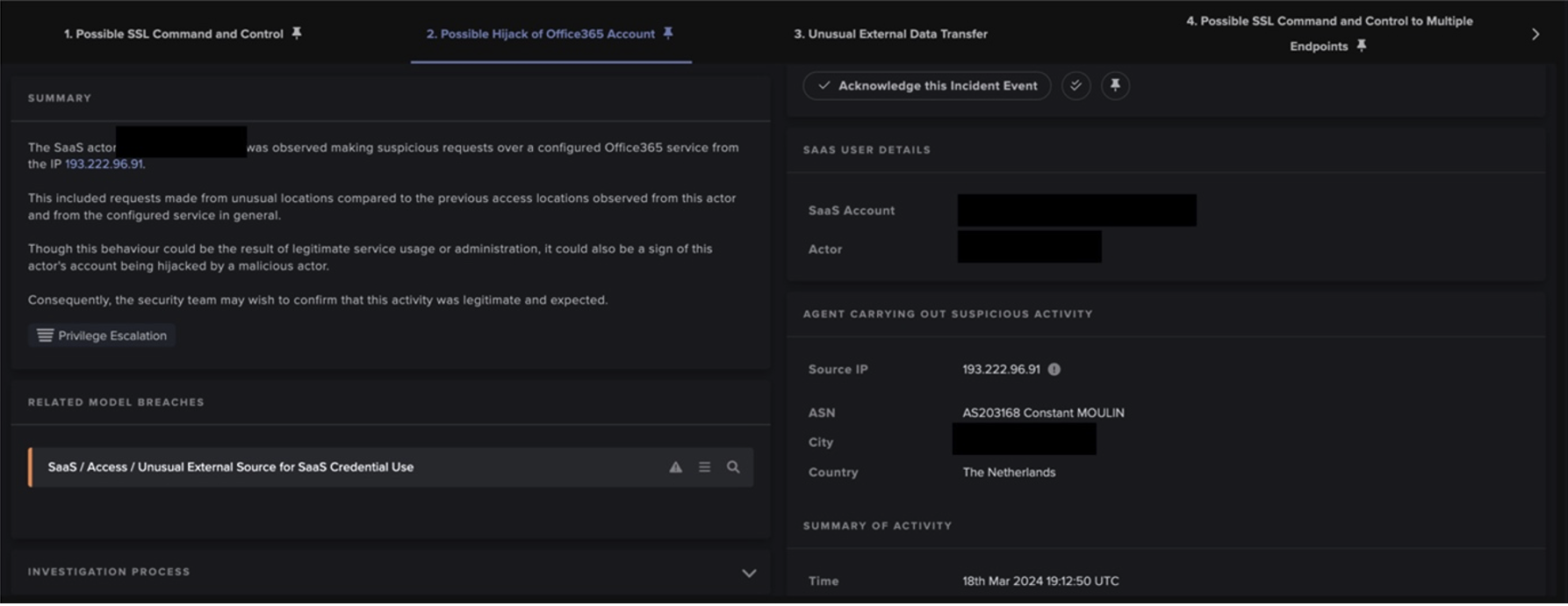
Microsoft Outlook 15.0 のような異常なユーザーエージェントがSMTP接続に使用されており、送信メールの件名の一部にBase64エンコードされた文字列が含まれていることが確認されました。さらに、このJA3クライアントのフィンガープリント(37cdab6ff1bd1c195bacb776c5213bf2)は、SSL接続からよく見受けられました。少なくとも10件の展開で観測されたマルウェアスパムのホスト名一式に基づくと、TLDは.jp、.com、.net、.mxが大半で、日本のTLDが最も多くなっています(図4)。

スパムモジュールから生成された平文のスパムコンテンツがPCAPで確認されました(図5)。フィッシングやスパムの明らかな指標となる例としては、1) 個人ヘッダーとEメールヘッダーの不一致、2) 件名における異常な返信チェーンと受信者の参照、3) 疑わしい圧縮ファイルの添付(例:Electronic form[.]zip.)があります。

4. ミッションの達成
Emotetの復活は、CobaltStrikeに関連する異常なSMBドライブ書き込みを伴う二次的な侵害でも示されました。これには、SSLアクティビティに見られる以下のJA3ハッシュ(72a589da586844d7f0818ce684948eea)や、svchost.exeファイルを含むSMB書き込みなどが一貫して含まれています。
Darktrace による検知
Emotetの復活に伴う活動を特定するために使用された主要なDETECT モデルは、可能性のあるC2を決定することに重点を置いていました。これらは以下の通りです:
· Suspicious SSL Activity
· Suspicious Self-Signed SSL
· Rare External SSL Self-Signed
· Possible Outbound Spam
ファイルにフォーカスする有益なモデルも含まれていました:
· Zip or Gzip from Rare External Location
· EXE from Rare External Location
Darktraceの検知能力は、脅威研究チームの調査で判明したケーススタディのサンプルでも示すことができます。
ケーススタディ
DarktraceのEmotet活動の検知は、業種や企業規模に制限されることなく行われました。新しいエポックでは、多くの類似した特徴が見られましたが、各インシデントではキャンペーンとは異なる手法が見られました。これは、以下の2つのクライアント環境において示されています。
行政機関の大規模な顧客環境を調査したところ、16種類のデバイスがexample[.]comという発行元と52,536回のSSL接続を行ったことが検知されました。この発行者に関連するデバイスは、主に同じ自己署名およびスパムに関するDETECT モデルを破っていることが確認されました。このSSLの前に異常な受信オクテットストリームが観察されましたが、ダウンロードとEmotet C2接続の間には明確な関係はありませんでした。影響を受けたデバイスはネットワーク全体のごく一部に過ぎないにもかかわらず、Darktrace アナリストは、はるかに大きなネットワーク「ノイズ」に対してフィルターをかけ、侵害の詳細な証拠を突き止めて、顧客に通知することができました。
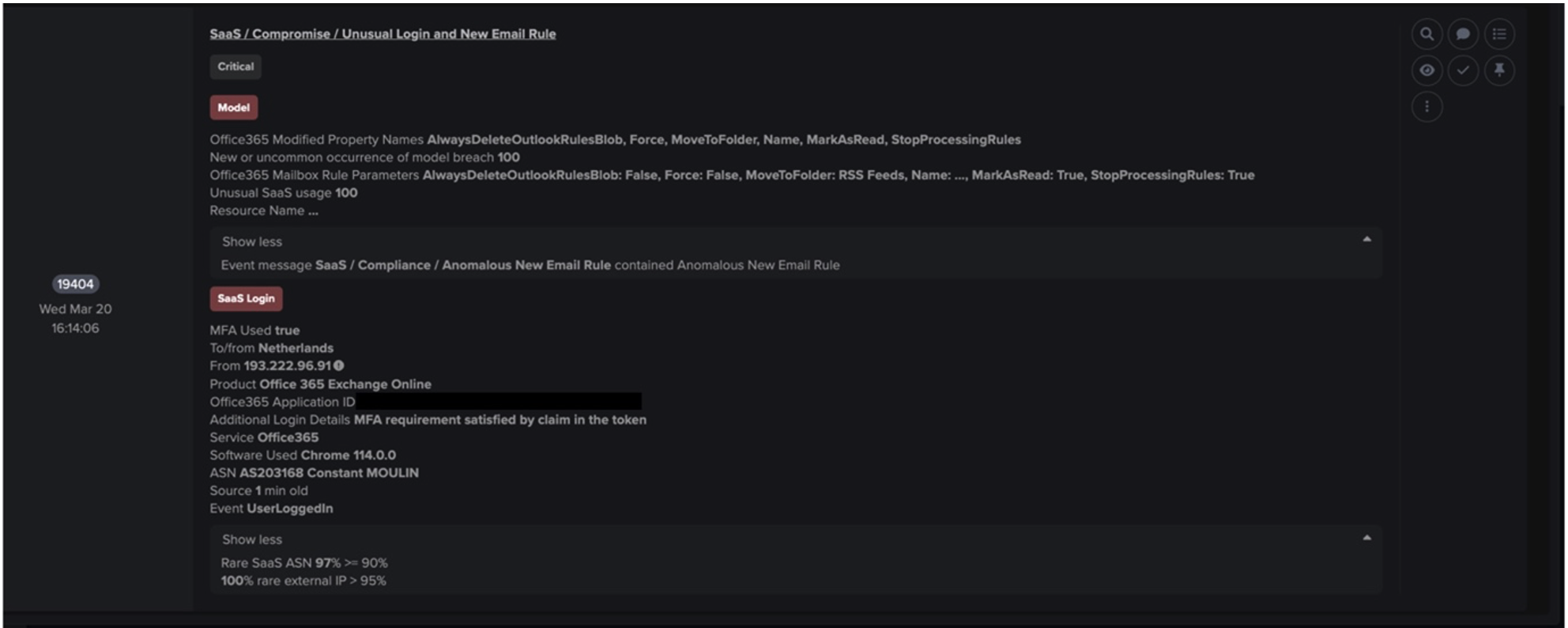
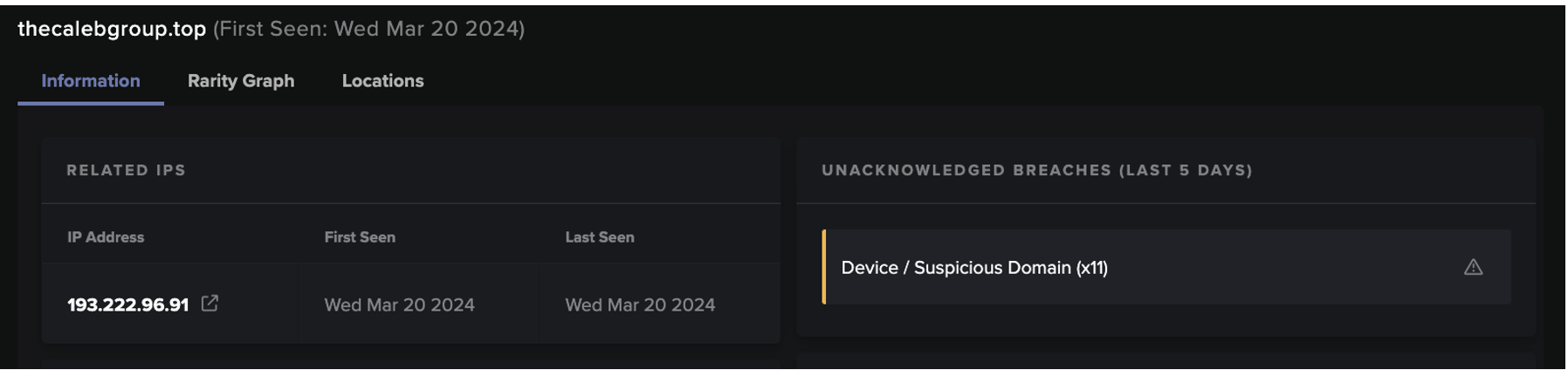
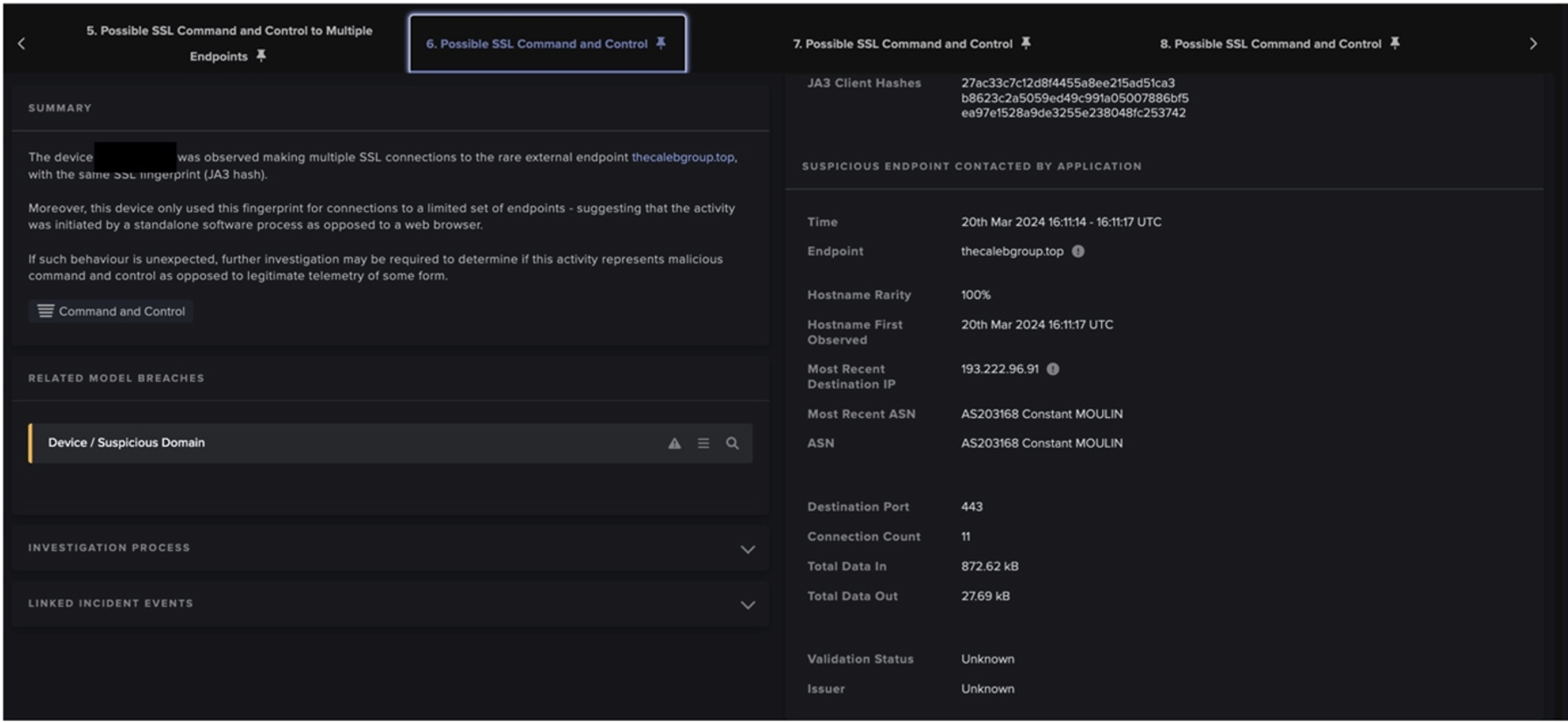
Darktrace はまた、より小規模な顧客環境における新たなEmotetの活動も確認しました。ヘルスケアおよび製薬分野のある企業を見てみると、2022年3月中旬から、単一の内部デバイスがホストarkpp[.]comに対してHTTP GETリクエストを行い、SHA256ハッシュを持つアルゴリズム生成DLL、TpipJHy7P.dllを含むことが検知されています。40060259d583b8cf83336bc50cc7a7d9e0a4de22b9a04e62ddc6ca5dedd6754b (図6).

サンプルがダウンロードされた後、デバイスは、ネットワーク上のデバイスから一度も接触したことのない多数のエンドポイントに接触しました。エンドポイントは、Emotet関連のIOCと前述の同じSSL証明書を含むポート443、8080、および7080を介して接触していました。また、同様の時間帯にマルウェアスパムの活動も観察されました。
上記の Emotet のケーススタディは、従来のルールやシグネチャに依存することなく、一連の異常な活動を 自律的に検知することで、いかに重要な脅威の活動を明らかにできるかを示しています。ステージングされたペイロードの可能性は、影響を受けた環境の一部でしか見られませんでしたが、多くのエンドポイントやポートを含む以下のアウトバウンドC2およびマルウェアスパム活動は、Emotetの検知に十分なものでした。
このような場合、Darktraceの自律遮断技術(RESPOND)は、段階的なペイロード、外部へのC2通信、マルウェアスパム活動に関連する活動を正確にターゲットとするピンポイントな処置を推奨または実施することになります。さらに、デバイスの通常の生活パターンを制限することで、同時に発生する悪意ある活動を防ぐと同時に、通常のビジネスオペレーションの継続を可能にします。
結論
- 過去と現在のEmotetの系統の技術的な違いは、悪意のある脅威アクターの多様性を強調し、シグネチャに依存しないセキュリティソリューションの必要性を示しています。
-Darktraceの可視化能力と独自の振る舞い検知により、ルールやシグネチャに依存することなく、新たなEmotet 株に関連するネットワーク活動の可視化を継続的に実現しています。主な例として、新しいEmotetのインフラへのC2接続があります。
- 今後は、疑わしいDLLを使用したC2確立を検知することで、Emotet株のネットワーク上でのさらなる伝播を防ぐことができます。
- DarktraceのAIによる検知と遮断能力は、静的・動的コード解析によるEmotet株の分析、その後のルールとシグネチャの実装を含む従来の侵害後の研究を凌駕するものです。
Paul JenningsとHanah Darleyの本ブログへの寄稿に感謝します。
付録
モデルブリーチ
· Anomalous Connection / Anomalous SSL without SNI to New External
· Anomalous Connection / Application Protocol on Uncommon Port
· Anomalous Connection / Multiple Connections to New External TCP Port
· Anomalous Connection / Multiple Failed Connections to Rare Endpoint
· Anomalous Connection / Multiple HTTP POSTs to Rare Hostname
· Anomalous Connection / Possible Outbound Spam
· Anomalous Connection / Rare External SSL Self-Signed
· Anomalous Connection / Repeated Rare External SSL Self-Signed
· Anomalous Connection / Suspicious Expired SSL
· Anomalous Connection / Suspicious Self-Signed SSL
· Anomalous File / Anomalous Octet Stream (No User Agent)
· Anomalous File / Zip or Gzip from Rare External Location
· Anomalous File / EXE from Rare External Location
· Compromise / Agent Beacon to New Endpoint
· Compromise / Beacon to Young Endpoint
· Compromise / Beaconing Activity To External Rare
· Compromise / New or Repeated to Unusual SSL Port
· Compromise / Repeating Connections Over 4 Days
· Compromise / Slow Beaconing Activity To External Rare
· Compromise / SSL Beaconing to Rare Destination
· Compromise / Suspicious Beaconing Behaviour
· Compromise / Suspicious Spam Activity
· Compromise / Suspicious SSL Activity
· Compromise / Sustained SSL or HTTP Increase
· Device / Initial Breach Chain Compromise
· Device / Large Number of Connections to New Endpoints
· Device / Long Agent Connection to New Endpoint
· Device / New User Agent
· Device / New User Agent and New IP
· Device / SMB Session Bruteforce
· Device / Suspicious Domain
· Device / Suspicious SMB Scanning Activity




Darktrace をお使いのお客様で、Darktrace を使って Emotet をトリアージする方法についてもっと知りたい方は、こちらを参照してください。
参考文献
[1] https://blog.lumen.com/emotet-redux/
[2] https://blogs.vmware.com/security/2022/03/emotet-c2-configuration-extraction-and-analysis.html
[3] https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2022/05/04/attacking-emotets-control-flow-flattening/