What is Black Basta?
Over the past year, security researchers have been tracking a new ransomware group, known as Black Basta, that has been observed targeted organizations worldwide to deploy double extortion ransomware attacks since early 2022. While the strain and group are purportedly new, evidence seen suggests they are an offshoot of the Conti ransomware group [1].
The group behind Black Basta run a Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) model. They work with initial access brokers who will typically already have a foothold in company infrastructure to begin their attacks. Once inside a network, they then pivot internally using numerous tools to further their attack.
Black Basta Ransomware
Like many other ransomware actors, Black Basta uses double extortion as part of its modus operandi, exfiltrating sensitive company data and using the publication of this as a second threat to affected companies. This is also advertised on a dark web site, setup by the group to apply further pressure for affected companies to make ransom payments and avoid reputational damage.
The group also seems to regularly take advantage of existing tools to undertake the earlier stages of their attacks. Notably, the Qakbot banking trojan, seems to be the malware often used to gain an initial foothold within compromised environments.
Analysis of the tools, procedures and infrastructure used by Black Basta belies a maturity to the actors behind the ransomware. Their models and practices suggest those involved are experienced individuals, and security researchers have drawn possible links to the Conti ransomware group.
As such, Black Basta is a particular concern for security teams as attacks will likely be more sophisticated, with attackers more patient and able to lie low on digital estates for longer, waiting for the opportune moment to strike.
Cyber security is an infinite game where defender and attacker are stuck as cat and mouse; as new attacks evolve, security vendors and teams respond to the new indicators of compromise (IoCs), and update their existing rulesets and lists. As a result, attackers are forced to change their stripes to evade detection or sometimes even readjust their targets and end goals.
Anomaly Based Detection
By using the power of Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI, security teams are able to detect deviations in behavior. Threat actors need to move through the kill chain to achieve their aims, and in doing so will cause affected devices within networks to deviate from their expected pattern of life. Darktrace’s anomaly-based approach to threat detection allows it recognize these subtle deviations that indicate the presence of an attacker, and stop them in their tracks.
Additionally, the ecosystem of cyber criminals has matured in the last few decades. It is well documented how many groups now operate akin to legitimate companies, with structure, departments and governance. As such, while new attack methods and tactics do appear in the wild, the maturity in their business models belie the experience of those behind the attack.
As attackers grow their business models and develop their arsenal of attack vectors, it becomes even more critical for security teams to remain vigilant to anomalies within networks, and remain agnostic to underlying IoCs and instead adopt anomaly detection tools able to identify tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) that indicate attackers may be moving through a network, ahead of deployment of ransomware and data encryption.
Darktrace’s Coverage of Black Basta
In April 2023, the Darktrace Security Operations Center (SOC) assisted a customer in triaging and responding to an ongoing ransomware infection on their network. On a Saturday, the customer reached out directly to the Darktrace analyst team via the Ask the Expert service for support after they observed encrypted files and locked administrative accounts on their network. The analyst team were able to investigate and clarify the attack path, identifying affected devices and assisting the customer with their remediation. Darktrace DETECT™ observed varying IoCs and TTPs throughout the course of this attack’s kill chain; subsequent analysis into these indicators revealed this had likely been a case of Black Basta seen in the wild.
初期の侵入
The methods used by the group to gain an initial foothold in environments varies – sometimes using phishing, sometimes gaining access through a common vulnerability exposed to the internet. Black Basta actors appear to target specific organizations, as opposed to some groups who aim to hit multiple at once in a more opportunistic fashion.
In the case of the Darktrace customer likely affected by Black Basta, it is probable that the initial intrusion was out of scope. It may be that the path was via a phishing email containing an Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that launches malicious powershell commands; a noted technique for Black Basta. [3][4] Alternatively, the group may have worked with access brokers who already had a foothold within the customer’s network.
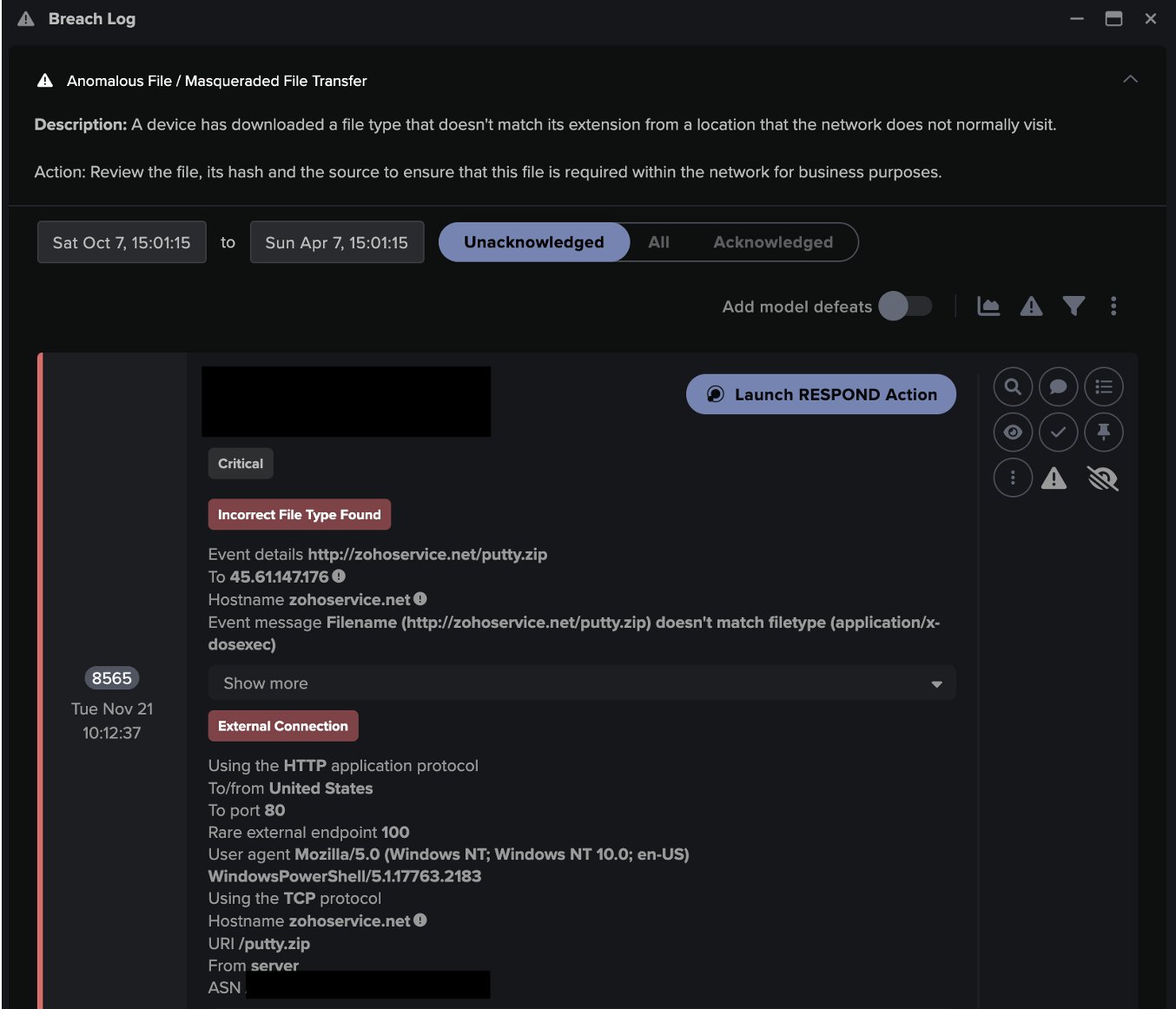
One particular device on the network was observed acting anomalously and was possibly the first to be infected. The device attempted to connect to multiple internal devices over SMB, and connected to a server that was later found to be compromised and is described throughout the course of this blog. During this connection, it wrote a file over SMB, “syncro.exe”, which is possibly a legitimate Remote Management software but could in theory be used to spread an infection laterally. Use of this tool otherwise appears sporadic for the network, and was notably unusual for the environment.
Given these timings, it is possible this activity is related to the likely Black Basta compromise. However, there is some evidence online that use of Syncro has been seen installed as part of the execution of loaders such as Batloader, potentially indicating a separate or concurrent attack [5].
Internal Reconnaissance + Lateral Movement
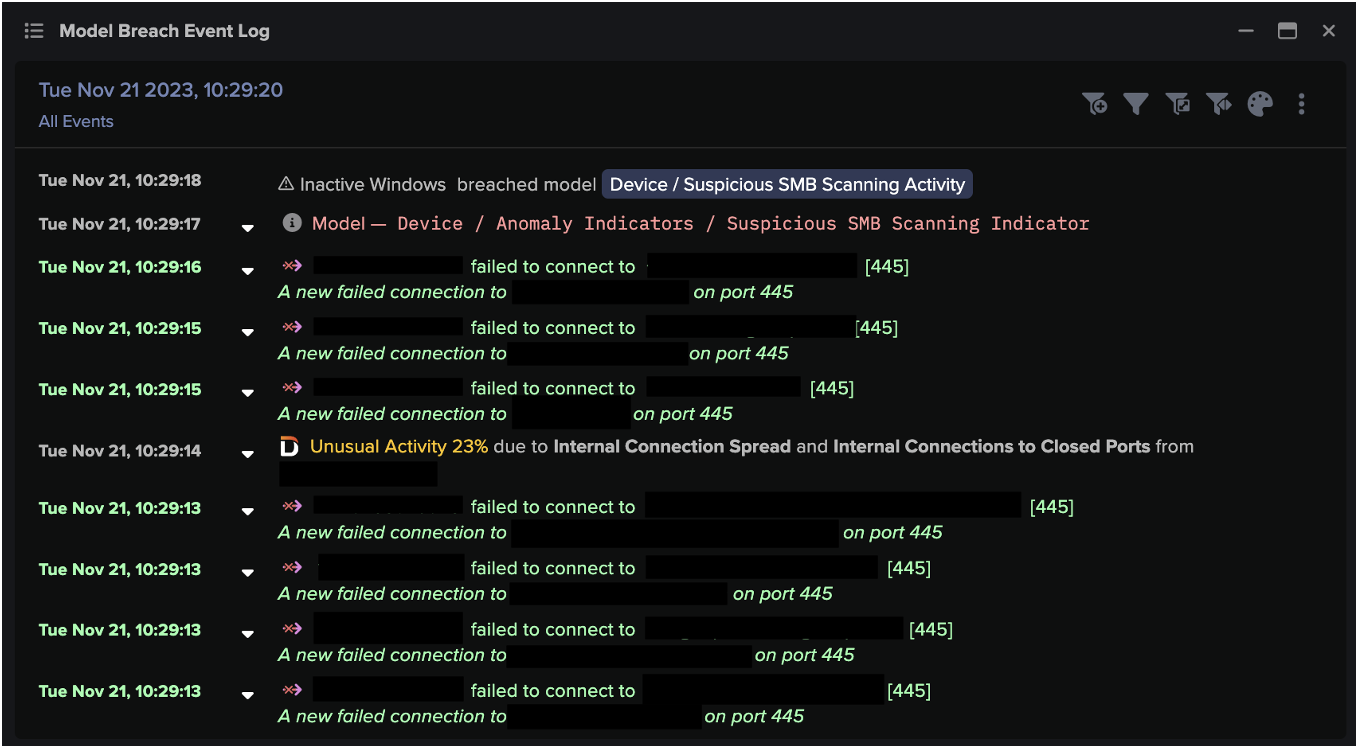
However the attackers gained access in this instance, the first suspicious activity observed by Darktrace originated from an infected server. The attacker used their foothold in the device to perform internal reconnaissance, enumerating large portions of the network. Darktrace DETECT’s anomaly detection noted a distinct rise in connections to a large number of subnets, particularly to closed ports associated with native Windows services, including:
- 135 (RPC)
- 139 (NetBIOS)
- 445 (SMB)
- 3389 (RDP)
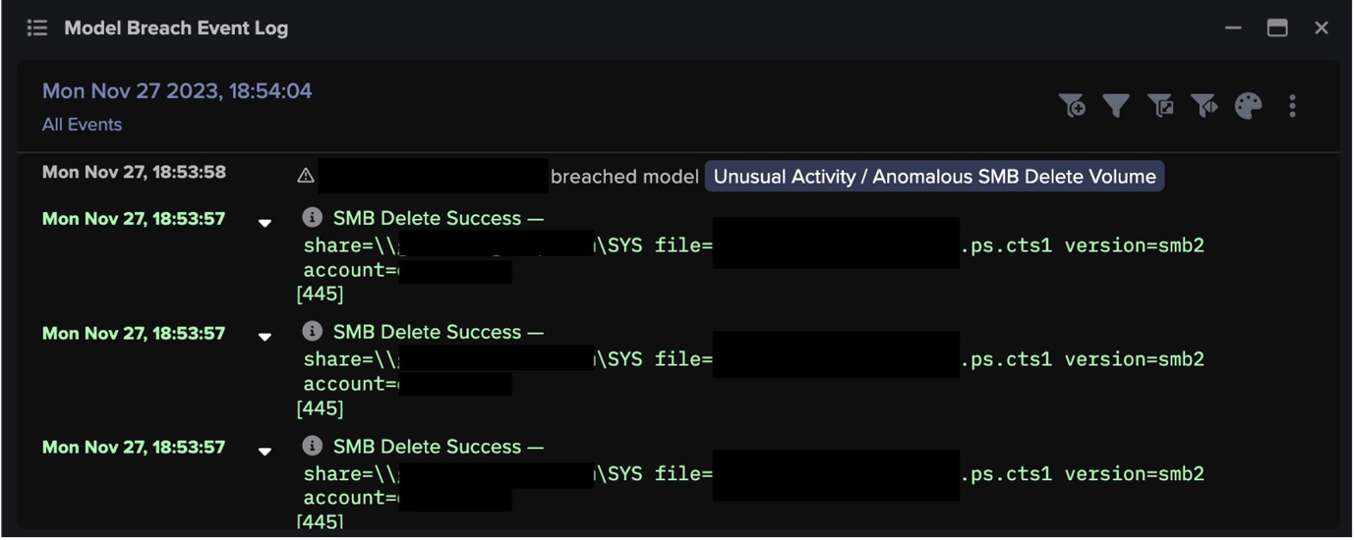
During the enumeration, SMB connections were observed during which suspiciously named executable files were written:
- delete.me
- covet.me
Data Staging and Exfiltration
Around 4 hours after the scanning activity, the attackers used their knowledge gained during enumeration about the environment to begin gathering and staging data for their double extortion attempts. Darktrace observed the same infected server connecting to a file storage server, and downloading over 300 GiB of data. Darktrace DETECT identified that the connections had been made via SMB and was able to present a list of filenames to the customer, allowing their security team to determine the data that had likely been exposed to the attackers.
The SMB paths detected by Darktrace showed a range of departments’ file areas being accessed by threat actors. This suggests they were interested in getting as much varied data as possible, presumably in an attempt to ensure a large amount of valuable information was at their disposal to make any threats of releasing them more credible, and more damaging to the company.
Shortly after the download, the device made an external connection over SSH to a rare domain, dataspt[.]com, hosted in the United States. The connection itself was made over an unusual port, 2022, and Darktrace recognized that the domain was new for the network.
During this upload, the threat actors uploaded a similar volume of data to the 300GiB that had been downloaded internally earlier. Darktrace flagged the usual elements of this external upload, making the identification and triage of this exfiltration attempt easier for the customer.
On top of this, Darktrace’s autonomous investigation tool Cyber AI Analyst™ launched an investigation into this on-going activity and was able to link the external upload events to the internal download, identifying them as one exfiltration incident rather than two isolated events. AI Analyst then provided a detailed summary of the activity detected, further speeding up the identification of affected files.
Preparing for Exploitation
All the activity documented so far had occurred on a Wednesday evening. It was at this point that the burst of activity calmed, and the ransomware lay in wait within the environment. Other devices around the network, particularly those connected to by the original infected server and a domain controller, were observed performing some elements of anomalous activity, but the attack seemed to largely take a pause.
However, on the Saturday morning, 3 days later, the compromised server began to change the way it communicated with attackers by reaching out to a new command and control (C2) endpoint. It seemed that attackers were gearing up for their attack, taking advantage of the weekend to strike while security teams often run with a reduced staffing.
Darktrace identified connections to a new endpoint within 4 minutes of it first being seen on the customer’s environment. The server had begun making repeated SSL connections to the new external endpoint, faceappinc[.]com, which has been flagged as malicious by various open-source intelligence (OSINT) sources.
The observed JA3 hash (d0ec4b50a944b182fc10ff51f883ccf7) suggests that the command-line tool BITS Admin was being used to launch these connections, another suggestion of the use of mature tooling.
In addition to this, Darktrace also detected the server using an administrative credential it had never previously been associated with. Darktrace recognized that the use of this credential represented a deviation from the device’s usual activity and thus could be indicative of compromise.
The server then proceeded to use the new credential to authenticate over Keberos before writing a malicious file (“management.exe”) to the Temp directory on a number of internal devices.
Encryption
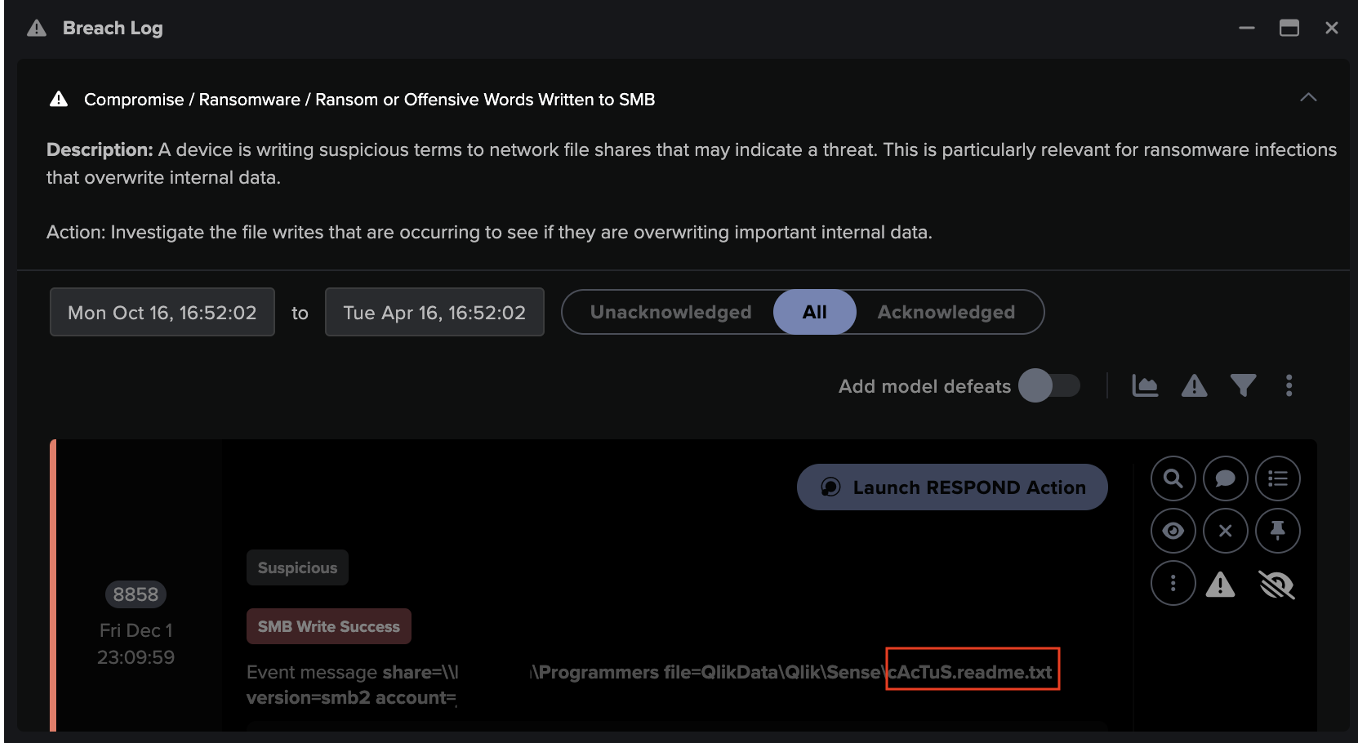
At this point, the number of anomalous activities detected from the server increased massively as the attacker seems to connect networkwide in an attempt to cause as quick and destructive an encryption effort as possible. Darktrace observed numerous files that had been encrypted by a local process. The compromised server began to write ransom notes, named “instructions_read_me.txt” to other file servers, which presumably also had successfully deployed payloads. While Black Basta actors had initially been observed dropping ransom notes named “readme.txt”, security researchers have since observed and reported an updated variant of the ransomware that drops “instructions_read_me_.txt”, the name of the file detected by Darktrace, instead [6].
Another server was also observed making repeated SSL connections to the same rare external endpoint, faceappinc[.]com. Shortly after beginning these connections, the device made an HTTP connection to a rare IP address with no hostname, 212.118.55[.]211. During this connection, the device also downloaded a suspicious executable file, cal[.]linux. OSINT research linked the hash of this file to a Black Basta Executable and Linkable File (ELF) variant, indicating that the group was highly likely behind this ransomware attack.
Of particular interest again, is how the attacker lives off the land, utilizing pre-installed Windows services. Darktrace flagged that the server was observed using PsExec, a remote management executable, on multiple devices.
Darktrace Assistance
Darktrace DETECT was able to clearly detect and provide visibility over all stages of the ransomware attack, alerting the customer with multiple model breaches and AI Analyst investigation(s) and highlighting suspicious activity throughout the course of the attack.
For example, the exfiltration of sensitive data was flagged for a number of anomalous features of the meta-data: volume; rarity of the endpoint; port and protocol used.
In total, the portion of the attack observed by Darktrace lasted about 4 days from the first model breach until the ransomware was deployed. In particular, the encryption itself was initiated on a Saturday.
The encryption event itself was initiated on a Saturday, which is not uncommon as threat actors tend to launch their destructive attacks when they expect security teams will be at their lowest capacity. The Darktrace SOC team regularly observes and assists in customer’s in the face of ransomware actors who patiently lie in wait. Attackers often choose to strike as security teams run on reduced hours of manpower, sometimes even choosing to deploy ahead of longer breaks for national or public holidays, for example.
In this case, the customer contacted Darktrace directly through the Ask the Expert (ATE) service. ATE offers customers around the clock access to Darktrace’s team of expert analysts. Customers who subscribe to ATE are able to send queries directly to the analyst team if they are in need of assistance in the face of suspicious network activity or emerging attacks.
In this example, Darktrace’s team of expert analysts worked in tandem with Cyber AI Analyst to investigate the ongoing compromise, ensuring that the investigation and response process were completed as quickly and efficiently as possible.
Thanks to Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI, the analyst team were able to quickly produce a detailed report enumerating the timeline of events. By combining the human expertise of the analyst team and the machine learning capabilities of AI Analyst, Darktrace was able to quickly identify anomalous activity being performed and the affected devices. AI Analyst was then able to collate and present this information into a comprehensive and digestible report for the customer to consult.
結論
It is likely that this ransomware attack was undertaken by the Black Basta group, or at least using tools related to their method. Although Black Basta itself is a relatively novel ransomware strain, there is a maturity and sophistication to its tactics. This indicates that this new group are actually experienced threat actors, with evidence pointing towards it being an offshoot of Conti.
The Pyramid of Pain is a well trodden model in cyber security, but it can help us understand the various features of an attack. Indicators like static C2 destinations or file hashes can easily be changed, but it’s the underlying TTPs that remain the same between attacks.
In this case, the attackers used living off the land techniques, making use of tools such as BITSAdmin, as well as using tried and tested malware such as Qakbot. While the domains and IPs involved will change, the way these malware interact and move about systems remains the same. Their fingerprint therefore causes very similar anomalies in network traffic, and this is where the strength of Darktrace lies.
Darktrace’s anomaly-based approach to threat detection means that these new attack types are quickly drawn out of the noise of everyday traffic within an environment. Once attackers have gained a foothold in a network, they will have to cause deviation from the usual pattern of a life on a network to proceed; Darktrace is uniquely placed to detect even the most subtle changes in a device’s behavior that could be indicative of an emerging threat.
Machine learning can act as a force multiplier for security teams. Working hand in hand with the Darktrace SOC, the customer was able to generate cohesive and comprehensive reporting on the attack path within days. This would be a feat for humans alone, requiring significant resources and time, but with the power of Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI, these deep and complex analyses become as easy as the click of a button.
Credit to: Matthew John, Director of Operations, SOC, Paul Jennings, Principal Analyst Consultant
付録
Darktrace DETECT Model Breaches
内部偵察
Device / Multiple Lateral Movement Model Breaches
Device / Large Number of Model Breaches
Device / Network Scan
Device / Anomalous RDP Followed by Multiple Model Breaches
Device / Possible SMB/NTLM Reconnaissance
Device / SMB Lateral Movement
Anomalous Connection / SMB Enumeration
Anomalous Connection / Possible Share Enumeration Activity
Device / Suspicious SMB Scanning Activity
Device / RDP Scan
Anomalous Connection / Active Remote Desktop Tunnel
Device / Increase in New RPC Services
Device / ICMP Address Scan
Download and Upload
Unusual Activity / Enhanced Unusual External Data Transfer
Unusual Activity / Unusual External Data Transfer
Anomalous Connection / Uncommon 1 GiB Outbound
Anomalous Connection / Data Sent to Rare Domain
Anomalous Connection / Download and Upload
Compliance / SSH to Rare External Destination
Anomalous Server Activity / Rare External from Server
Anomalous Server Activity / Outgoing from Server
Anomalous Connection / Application Protocol on Uncommon Port
Anomalous Connection / Multiple Connections to New External TCP Port
Device / Anomalous SMB Followed By Multiple Model Breaches
Unusual Activity / SMB Access Failures
Lateral Movement and Encryption
User / New Admin Credentials on Server
Compliance / SMB Drive Write
Device / Anomalous RDP Followed By Multiple Model Breaches
Anomalous Connection / High Volume of New or Uncommon Service Control
Anomalous Connection / New or Uncommon Service Control
Device / New or Unusual Remote Command Execution
Anomalous Connection / SMB Enumeration
Additional Beaconing and Tooling
Device / Initial Breach Chain Compromise
Device / Multiple C2 Model Breaches
Compromise / Large Number of Suspicious Failed Connections
Compromise / Sustained SSL or HTTP Increase
Compromise / SSL or HTTP Beacon
Compromise / Suspicious Beaconing Behavior
Compromise / Large Number of Suspicious Successful Connections
Compromise / High Volume of Connections with Beacon Score
Compromise / Slow Beaconing Activity To External Rare
Compromise / SSL Beaconing to Rare Destination
Compromise / Beaconing Activity To External Rare
Compromise / Beacon to Young Endpoint
Compromise / Agent Beacon to New Endpoint
Anomalous Server Activity / Rare External from Server
Anomalous Connection / Multiple Failed Connections to Rare Endpoint
Anomalous File / EXE from Rare External Location
IoC - Type - Description + Confidence
dataspt[.]com - Hostname - Highly Likely Exfiltration Server
46.22.211[.]151:2022 - IP Address and Unusual Port - Highly Likely Exfiltration Server
faceappinc[.]com - Hostname - Likely C2 Infrastructure
Instructions_read_me.txt - Filename - Almost Certain Ransom Note
212.118.55[.]211 - IP Address - Likely C2 Infrastructure
delete[.]me - Filename - Potential lateral movement script
covet[.]me - Filename - Potential lateral movement script
d0ec4b50a944b182fc10ff51f883ccf7 - JA3 Client Fingerprint - Potential Windows BITS C2 Process
/download/cal.linux - URI - Likely BlackBasta executable file
1f4dcfa562f218fcd793c1c384c3006e460213a8 - Sha1 File Hash - Likely BlackBasta executable file

参考文献
[1] https://blogs.blackberry.com/en/2022/05/black-basta-rebrand-of-conti-or-something-new
[2] https://www.cybereason.com/blog/threat-alert-aggressive-qakbot-campaign-and-the-black-basta-ransomware-group-targeting-u.s.-companies
[4] https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/atoms/blackbasta-ransomware/
[6] https://www.pcrisk.com/removal-guides/23666-black-basta-ransomware































![Cyber AI Analyst Incident Log showing the offending device making over 1,000 connections to the suspicious hostname “zohoservice[.]net” over port 8383, within a specific period.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/662971c1cf09890fd46729a1_Screenshot%202024-04-24%20at%201.55.10%20PM.png)